Data Access at FLASH (DAQ, gpfs,...)
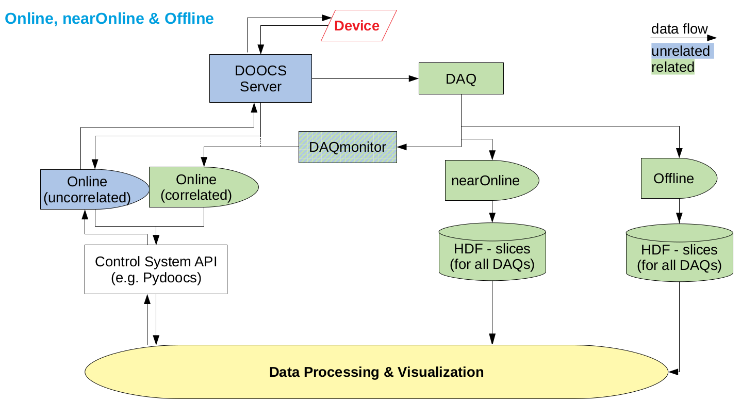
At the Free-electron Laser Hamburg (FLASH) we use the Distributed Object Oriented Control System (DOOCS). Devices are implemented via DOOCS servers and via an API it is possible to request data directly from the DOOCS server by knowing the DOOCS address.
As correlations of different physical properties are often required all data at FLASH are indexed by the train ID, which identifies each pulse train. The data recorded during a beamtime are stored via a Data Acquisition System (DAQ) which sorts all events from the individual DOOCS server by train ID. When requested HDF files are created after the beamtime which include the important data from the accelerator and its diagnostic as well as the data created by the users. This time scale we define as offline as the HDF files are converted after the beamtime is over. For synchronous data during an experiment it is possible to create HDF slices via a nearOnline converter within a few minutes. Reading synchronous data via an online API is possible via a configurable DAQ middle layer server, the DAQmonitor, which feeds the correlated data back in the control system while it provides a ring buffer with 32 events in size.
online | live at 10 Hz |
online via DAQmonitor | live up to 3s into the past |
nearOnline | a few minutes |
offline | after the beamtime |

During a beamtime at FLASH we have two IT infrastructures each with different purpose. In the FLASH halls you have local machines which are used with functional accounts and they have access to the beamline files-system for your current experiment. For more demanding task we could also provide workstations which can be dedicated to a single user experiment. For offline and nearOnline analysis the Maxwell cluster for high performance computing is available. On the Maxwell cluster you have to work with personal accounts as this regulates data access to the core file-system.
